Introduction
Foreign Exchange (Forex) trading, with its immense liquidity and 24/5 accessibility, offers significant opportunities for profit. However, it also inherently carries substantial risks. Effective risk management is not merely a suggestion but a critical discipline that separates successful traders from those who face significant losses. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of risk management in Forex trading, detailing essential strategies and tools for both novice and experienced traders to navigate the volatile currency markets successfully.
Understanding Forex Risk Management
Forex risk management involves implementing a set of rules and measures designed to minimize potential losses and protect trading capital. It is a proactive approach that requires careful planning and discipline, ensuring that any negative impact from market movements remains manageable [2]. The primary goal is to preserve capital, reduce emotional stress, and ensure long-term sustainability in an unpredictable trading environment [1].
What is Forex Risk?
Forex risk, or currency risk, refers to the potential for financial losses due to adverse movements in exchange rates. For individual traders, this can directly impact the profitability of their positions. For larger entities, such as multinational corporations or public debt managers, foreign currency risk can significantly affect valuations, profitability, and overall financial performance [1]. Exchange rates are among the most volatile financial variables, and their movements can rapidly alter the value of outstanding debt and servicing costs [3].
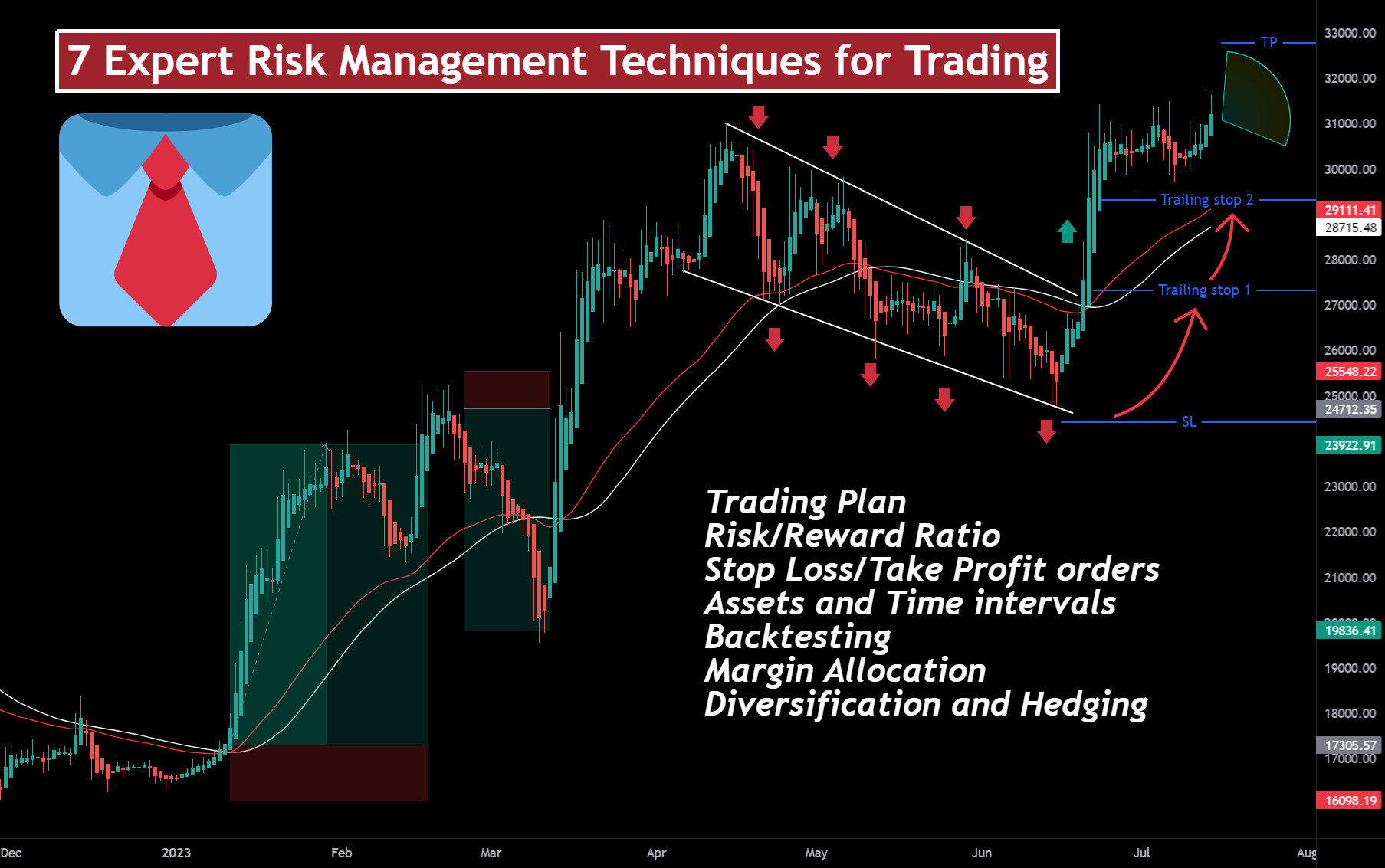
Key Risk Management Strategies
A robust risk management strategy is built upon several fundamental principles and practices. Implementing these strategies can help traders mitigate potential losses and enhance their chances of long-term success.
1. Develop a Comprehensive Trading Plan
A well-defined trading plan is the cornerstone of effective risk management. It acts as a personal decision-making tool, outlining what, when, why, and how much to trade [2]. This plan should be highly personalized, reflecting individual goals, risk tolerance, available capital, and time commitment. It helps maintain discipline and prevents impulsive decisions driven by market volatility or emotions. Maintaining a trading diary to record entry/exit points and emotional states can further refine this plan over time [2].
2. Understand and Manage Leverage
Leverage is a double-edged sword in Forex trading. While it allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital (margin), it also magnifies both potential profits and losses [2]. Understanding how leverage works and its implications is crucial. Traders should use leverage judiciously, aligning it with their risk tolerance and overall trading strategy. Over-leveraging is a common pitfall that can lead to rapid capital depletion.
3. Implement Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
Stop-loss orders are indispensable tools for limiting potential losses. They automatically close a trade when the market price reaches a predetermined level, preventing further adverse movement [2, 4]. Traders should set stop-loss orders based on their comfort zone and technical analysis, rather than arbitrary price levels. Different types of stop orders include:
- Normal Stops: Close a position if the market moves against the trader, though slippage can occur in volatile markets [2].
- Guaranteed Stops: Ensure the position is closed at the exact specified price, eliminating slippage risk [2].
- Trailing Stops: Follow positive price movements and adjust automatically, locking in profits while still protecting against reversals [2].
Take-profit orders, conversely, automatically close a trade when a predetermined profit target is reached. This helps traders lock in gains and avoid the temptation of holding onto a winning trade for too long, which can lead to reversals [2].
4. Determine a Favorable Risk-Reward Ratio
Before entering any trade, it is essential to calculate the risk-reward ratio. This ratio compares the potential loss on a trade to its potential gain [2]. A favorable risk-reward ratio, such as 1:2 or 1:3 (meaning potential profit is two or three times the potential loss), ensures that even if not every trade is successful, overall profitability can be maintained. For example, with a 1:3 ratio, a trader can be profitable even if only 30% of their trades are successful [2].
5. Position Sizing
Position sizing involves determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to each trade. A common rule of thumb is the
1% or 2% rule, where a trader risks no more than 1% or 2% of their total trading capital on any single trade [3]. This approach helps protect the trading account from significant drawdowns due to a series of losing trades.
6. Diversification
While Forex trading primarily involves currency pairs, diversification can still be applied by not over-concentrating on a single currency pair or trading strategy. Spreading risk across different, uncorrelated currency pairs can help mitigate the impact of adverse movements in one particular market. However, it’s important to note that true diversification in Forex can be challenging due to the interconnected nature of global currencies.
7. Manage Your Emotions
Emotional control is a critical, yet often overlooked, aspect of risk management. Fear, greed, and overconfidence can lead to impulsive decisions that deviate from a well-thought-out trading plan [2]. Developing emotional discipline, sticking to the trading plan, and avoiding revenge trading are essential for consistent performance. Taking breaks, reviewing past trades, and understanding personal psychological biases can help in managing emotions effectively.
8. Stay Informed and Adapt
The Forex market is constantly influenced by global economic events, geopolitical developments, and central bank policies. Staying informed about these factors is crucial for anticipating market movements and adjusting trading strategies accordingly [2]. Economic calendars, news feeds, and market analysis reports can provide valuable insights. However, it’s equally important to filter information and avoid being overwhelmed by noise, focusing on data that directly impacts chosen currency pairs.
Tools for Forex Risk Management
Beyond strategic principles, several practical tools aid in effective Forex risk management:
- Trading Platforms: Modern trading platforms like MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5) offer advanced charting tools, technical indicators, and automated trading capabilities that assist in analyzing markets and executing risk management strategies [5].
- Risk Calculators: Many brokers and third-party providers offer risk calculators that help traders determine appropriate position sizes and potential risk per trade based on their account balance and stop-loss levels.
- Economic Calendars: These calendars highlight upcoming economic data releases and events that can impact currency markets, allowing traders to anticipate volatility and adjust their strategies.
- Trading Journals: As mentioned earlier, a trading journal is an invaluable tool for tracking trades, analyzing performance, and identifying patterns or mistakes in trading behavior.
Conclusion
Risk management is an indispensable component of successful Forex trading. By understanding the inherent risks, developing a comprehensive trading plan, judiciously using leverage, implementing stop-loss and take-profit orders, and maintaining emotional discipline, traders can significantly enhance their chances of long-term profitability. The dynamic nature of the Forex market demands continuous learning, adaptation, and a steadfast commitment to sound risk management principles. While no strategy can eliminate risk entirely, a well-executed risk management framework provides the necessary protection and structure to navigate the complexities of currency trading effectively.
References
- [1] Al Mansoori, Ghareeba Hamad, et al. “Foreign Exchange Risk Management: A Comprehensive Literature Review and Mitigation Strategies in Floating Exchange Rate Regimes.” *ResearchGate*, January 2024. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/386147590_Foreign_Exchange_Risk_Management_A_Comprehensive_Literature_Review_and_Mitigation_Strategies_in_Floating_Exchange_Rate_Regimes
- [2] IG International. “Eight Forex Risk Management Strategies for Beginners.” *IG.com*. Available at: https://www.ig.com/en/trading-strategies/top-risk-management-strategies-in-forex-trading-200630
- [3] Jonasson, Thordur, et al. “Managing Foreign Exchange Rate Risk: Capacity Development for Public Debt Managers in Emerging Market and Low-Income Countries.” *IMF Working Paper*, August 2024. Available at: https://www.imf.org/-/media/files/publications/wp/2024/english/wpiea2024167-print-pdf.pdf
- [4] Investopedia. “Understanding Forex Risk Management.” *Investopedia.com*. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/articles/forex/10/forex-risk-management.asp
- [5] Axi. “Forex Risk Management Trading Strategies.” *Axi.com*. Available at: https://www.axi.com/int/blog/education/forex/forex-risk-management-trading-strategies